What are the Key Components of Topographic Surveys?
Introduction
Topographic surveys are crucial for various industries, from civil engineering and construction to environmental management and urban planning. These surveys provide detailed information about the natural and man-made features of a piece of land, allowing BIM Company to make informed decisions. In this comprehensive guide, we will understand what’s included in a topographic survey, why they are essential, and how they are conducted.
What Is a Topographic Survey?
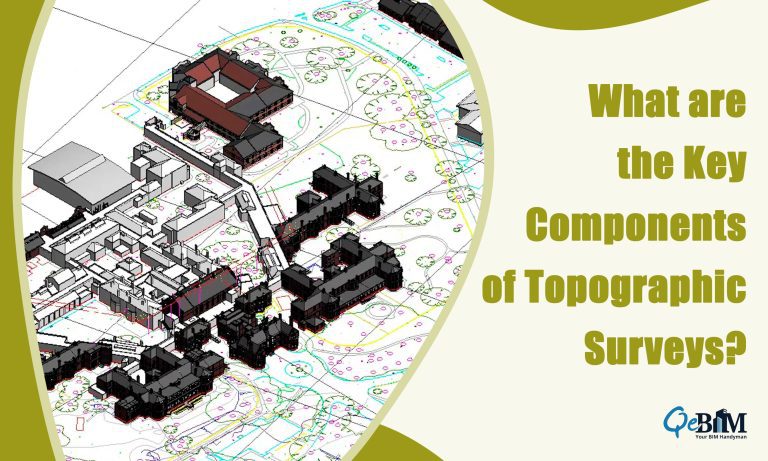
A topographic survey, often referred to as a contour survey, is a specialized land survey that accurately maps the three-dimensional shape and features of a piece of land using accurate Point Cloud to BIM Services. The primary objective is to represent the existing conditions of the land’s surface, showing its elevation, contours, and key features. Topographic surveys are critical in a wide range of applications, including:
- Land Development: Before designing and constructing structures, developers need a thorough understanding of the site’s topography to plan efficiently.
- Civil Engineering: Infrastructure projects such as roads, bridges, and drainage systems require precise topographic data for design and construction.
- Environmental Assessments: Topographic surveys help in environmental impact assessments, ensuring sustainable development and conservation of natural resources.
- Urban Planning: Municipalities use topographic data to create zoning plans, regulate land use, and manage urban growth.
- Landscaping: Landscape architects employ topographic surveys to create outdoor spaces that are both visually appealing and practical.
Now that we understand the importance of topographic surveys, let’s dive into what’s included in these surveys.
Key Components of a Topographic Survey
- Elevation Data: This is the most critical component of a topographic survey. It involves measuring and recording the elevation or height of various points on the land surface. These points are typically represented as contour lines on a topographic map, helping to visualize the terrain’s shape.
- Contour Lines: Contour lines are one of the most recognizable features of a topographic map. These lines connect points of equal elevation and provide a clear depiction of the land’s shape. The spacing between contour lines, known as the contour interval, depends on the scale of the map and the steepness of the terrain.
- Natural Features: Topographic surveys include the identification and mapping of natural features such as rivers, lakes, streams, forests, and vegetation. These features are essential for understanding the land’s ecological significance.
- Man-Made Structures: Man-made features are equally important and include buildings, roads, bridges, utility poles, fences, and other structures. This information helps in planning and design by ensuring that new developments can coexist with existing structures.
- Utilities: Underground utilities like water and sewer lines, gas pipes, and electrical conduits are typically located during a topographic survey. This information is crucial for avoiding conflicts during construction and excavation.
- Soil Types: Understanding the composition and characteristics of the soil on a site is vital for engineering purposes. Soil data aids in establishing foundation design, load-bearing capacity, and construction methodologies.
- Legal Boundaries: While primarily focused on the land’s physical features, topographic surveys also include boundary information, ensuring that the project stays within legal property lines.
- Geodetic Control Points: These are reference points with known coordinates used to establish a coordinate system for the survey. Geodetic control points help ensure the survey’s accuracy and compatibility with other geospatial data.
The Process of Conducting a Topographic Survey
Now that we’ve covered what’s included in a topographic survey, let’s explore the process of conducting one:
- Project Planning: The first step involves defining the objectives of the survey and the area to be surveyed. The surveyor collaborates with the client to understand specific requirements.
- Field Work: Surveyors visit the site to collect data. This may involve using various instruments such as total stations, GPS receivers, and LiDAR technology. They measure elevations, distances, and positions of various points on the land.
- Data Processing: Once the field data is collected, it is processed and organized. This step often involves the use of specialized software to create detailed topographic maps and digital elevation models (DEMs).
- Map Production: The processed data is used to create topographic maps and reports, which provide a visual representation of the land’s features, contours, and other important details.
- Quality Control: To ensure accuracy, quality control checks are carried out, including comparing the topographic survey data with existing records and ensuring that it meets project specifications.
- Client Deliverables: The final survey results are delivered to the client in a format that suits their needs. This may include paper maps, digital files, or interactive web-based platforms.
The Importance of Accurate Topographic Surveys
Accurate topographic surveys are vital for several reasons:
- Safety: Inaccurate elevation data or missing details can lead to safety hazards during construction, as structures might not be adequately supported or drainage systems might fail.
- Cost Efficiency: Precise topographic surveys help reduce the risk of unexpected construction challenges and costly changes during the project, ultimately saving time and money.
- Environmental Impact: Topographic surveys contribute to responsible land development by assessing and minimizing environmental impacts.
- Urban Planning: Cities and municipalities rely on topographic surveys to make informed decisions about land use, infrastructure development, and resource management.
- Legal Compliance: Ensuring that projects adhere to property boundaries and zoning regulations is essential to avoid legal disputes and liabilities.
Conclusion
Topographic surveys are invaluable tools that offer an in-depth insight into the land’s attributes. By accurately representing elevation, contours, and various features, these surveys play a critical role in land development, civil engineering, environmental management, and urban planning. Whether you’re a developer, engineer, environmentalist, or urban planner, understanding what’s included in a topographic survey and the process involved is essential for making informed decisions and ensuring the success of your projects.